Java Client Tutorial¶

The Sentilo Java Client is a library developed for working with webapps or standalone java applications. You can download an example of a client from https://github.com/sentilo/sentilo-client-sample-java.
For this example, we’ll use a basic maven based web application, that retrieve some system data and send it as a sensor observation to the Sentilo Platform. This webapp is named sentilo-client-java-sample and you’ll find it into the source code (see above).
Hardware¶
We don’t need any specific hardware for running this example, only one PC with Internet connection.
Software¶
You’ll need some software packages, as you’re developing in Java environment:
- Java SE 1.8
- Eclipse IDE or STS Spring IDE
- The Sentilo Client Java Library, which you can download and install it as a Maven dependency into your project (please, see the pom file in the project form more information)
- Tomcat 7+
- If you don’t have access to a working Sentilo instance, you might as well use our ` Sentilo VM </use_a_virtual_machine.html>`__.
The example¶
The code¶
Please download this sample webapp project from Git repository: https://github.com/sentilo/sentilo-client-sample-java
Once you have the project, open it with Eclipse or another IDE and construct it using Maven goals: clean package, for downloading dependencies, compile the code and package it.
After your project is compiled and packaged, you can deploy it in a Tomcat webapp container (standalone or the one your IDE provides).
Note
In case you use our VM on the same machine as Tomcat of this example, you might have a problem with port 8080 already being used. That’s because Virtualbox will NAT the VM’s Tomcat on 8080 to port 8080 on your host machine. If it’s your case, you should change the port of your Tomcat to, for example, 8888.
Now you can then navigate into the project and edit the source code.
The properties file¶
You must modify the properties file application.properties located
in src/main/resources/properties in order to provide your correct
Sentilo Platform Client configurations.
# Sentilo Platform API Services IP
rest.client.host=YOUR_SENTILO_PLATFORM_CLIENT_ADDRESS
# User configurations
rest.client.identityKey=YOUR_IDENTITY_KEY
rest.client.provider=samples-provider
rest.client.component=sample-component
rest.client.component.type=generic
rest.client.component.location=41.387015 2.170047
rest.client.sensor=sample-sensor-java
rest.client.sensor.type=status
rest.client.sensor.dataType=TEXT
rest.client.sensor.location=41.387015 2.170047
This settings should be updated:
- rest.client.host: provide a correct host or ip address of your Sentilo Platform Client, and replace the YOUR_SENTILO_PLATFORM_CLIENT_ADDRESS with it. Needs the protocol and the port. Ex: http://localhost:8081
- rest.client.identityKey: provide your correct application security token, and replace the YOUR_IDENTITY_KEY with it
- optionally rest.client.sensor.type: you can select a default type (anemometer, humidity, noise… etc) in the catalog or you can create one of your election there.
- optionally, you can provide your component / sensor locations, modifying the values rest.client.component.location and rest.client.sensor.location
The samples controller¶
There’s a Spring MVC controller which displays a view with the sensor data retrieved from system and the publish result. Navigate to src/main/java and open this resource org.sentilo.samples.controller.SamplesController.
This is a Spring Framework Controller that creates a view where you’ll see a sample data value obtained from the System, and then send it as observation to your Sentilo Platform instance. The webapp is based on Maven & Spring foundations, so you must modify and provide some configurations before start the example execution (see above).
@Controller
public class SamplesController {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SamplesController.class);
private static final String VIEW_SAMPLES_RESPONSE = "samples";
@Autowired
private PlatformTemplate platformTemplate;
@Resource
private Properties samplesProperties;
@RequestMapping(value = {"/", "/home"})
public String runSamples(final Model model) {
// All this data must be created in the Catalog Application before start this
// sample execution. At least the application identity token id and the provider id must be
// declared in system twice
String restClientIdentityKey = samplesProperties.getProperty("rest.client.identityKey");
String providerId = samplesProperties.getProperty("rest.client.provider");
// For this example we have created a generic component with a status sensor that accepts text
// type observations, only for test purpose
String componentId = samplesProperties.getProperty("rest.client.component");
String sensorId = samplesProperties.getProperty("rest.client.sensor");
logger.info("Starting samples execution...");
String observationsValue = null;
String errorMessage = null;
try {
// Get some system data from runtime
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
NumberFormat format = NumberFormat.getInstance();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
long maxMemory = runtime.maxMemory();
long allocatedMemory = runtime.totalMemory();
long freeMemory = runtime.freeMemory();
sb.append("free memory: " + format.format(freeMemory / 1024) + "<br/>");
sb.append("allocated memory: " + format.format(allocatedMemory / 1024) + "<br/>");
sb.append("max memory: " + format.format(maxMemory / 1024) + "<br/>");
sb.append("total free memory: " + format.format((freeMemory + (maxMemory - allocatedMemory)) / 1024) + "<br/>");
// In this case, we're getting CPU status in text mode
observationsValue = sb.toString();
logger.info("Observations values: " + observationsValue);
// Create the sample sensor, only if it doesn't exists in the catalog
createSensorIfNotExists(restClientIdentityKey, providerId, componentId, sensorId);
// Publish observations to the sample sensor
sendObservations(restClientIdentityKey, providerId, componentId, sensorId, observationsValue);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error publishing sensor observations: " + e.getMessage(), e);
errorMessage = e.getMessage();
}
logger.info("Samples execution ended!");
model.addAttribute("restClientIdentityKey", restClientIdentityKey);
model.addAttribute("providerId", providerId);
model.addAttribute("componentId", componentId);
model.addAttribute("sensorId", sensorId);
model.addAttribute("observations", observationsValue);
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
try {
if (errorMessage != null && errorMessage.length() > 0) {
Object json = mapper.readValue(errorMessage, Object.class);
model.addAttribute("errorMsg", mapper.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter().writeValueAsString(json));
} else {
model.addAttribute("successMsg", "Observations sent successfully");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error parsing JSON: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
errorMessage += (errorMessage.length() > 0) ? "<br/>" : "" + e.getMessage();
model.addAttribute("errorMsg", errorMessage);
}
return VIEW_SAMPLES_RESPONSE;
}
/**
* Retrieve catalog information about the sample provider. If the component and/or sensor doesn't
* exists, then let create they
*
* @param identityToken Samples Application identity token for manage the rest connections
* @param providerId Samples provider id
* @param componentId Samples component id
* @param sensorId Samples sensor id
* @return {@link CatalogOutputMessage} object with provider's catalog data
*/
private CatalogOutputMessage createSensorIfNotExists(String identityToken, String providerId, String componentId, String sensorId) {
List<String> sensorsIdList = new ArrayList<String>();
sensorsIdList.add(sensorId);
// Create a CatalogInputMessage object for retrieve server data
CatalogInputMessage getSensorsInputMsg = new CatalogInputMessage();
getSensorsInputMsg.setProviderId(providerId);
getSensorsInputMsg.setIdentityToken(identityToken);
getSensorsInputMsg.setSensors(createSensorsList(providerId, componentId, sensorsIdList));
// Obtain the sensors list from provider within a CatalogOutputMessage response object type
CatalogOutputMessage getSensorsOutputMsg = platformTemplate.getCatalogOps().getSensors(getSensorsInputMsg);
// Search for the sensor in the list
boolean existsSensor = false;
if (getSensorsOutputMsg.getProviders() != null && !getSensorsOutputMsg.getProviders().isEmpty()) {
for (AuthorizedProvider provider : getSensorsOutputMsg.getProviders()) {
if (provider.getSensors() != null && !provider.getSensors().isEmpty()) {
for (CatalogSensor sensor : provider.getSensors()) {
logger.debug("Retrieved sensor: " + sensor.getComponent() + " - " + sensor.getSensor());
existsSensor |= sensorId.equals(sensor.getSensor());
if (existsSensor) {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// If the sensor doesn't exists in the retrieved list, we must create it before publish the
// observations
if (!existsSensor) {
// Create a CatalogInputMessage object for retrieve server data
CatalogInputMessage registerSensorsInputMsg = new CatalogInputMessage(providerId);
registerSensorsInputMsg.setIdentityToken(identityToken);
registerSensorsInputMsg.setSensors(createSensorsList(providerId, componentId, sensorsIdList));
// Register the new sensor in the server
platformTemplate.getCatalogOps().registerSensors(registerSensorsInputMsg);
}
return getSensorsOutputMsg;
}
/**
* Publish some observations from a sensor
*
* @param identityToken Samples Application identity token for manage the rest connections
* @param providerId Samples provider id
* @param componentId Samples component id
* @param sensorId Samples sensor id
* @param value Observations value, in our case, a String type
*/
private void sendObservations(String identityToken, String providerId, String componentId, String sensorId, String value) {
List<String> sensorsIdList = new ArrayList<String>();
sensorsIdList.add(sensorId);
createSensorsList(providerId, componentId, sensorsIdList);
List<Observation> observations = new ArrayList<Observation>();
Observation observation = new Observation(value, new Date());
observations.add(observation);
SensorObservations sensorObservations = new SensorObservations(sensorId);
sensorObservations.setObservations(observations);
DataInputMessage dataInputMessage = new DataInputMessage(providerId, sensorId);
dataInputMessage.setIdentityToken(identityToken);
dataInputMessage.setSensorObservations(sensorObservations);
platformTemplate.getDataOps().sendObservations(dataInputMessage);
}
/**
* Create a component list
*
* @param componentId Component identifier
* @return A {@link CatalogComponent} list
*/
private List<CatalogComponent> createComponentsList(String componentId) {
List<CatalogComponent> catalogComponentList = new ArrayList<CatalogComponent>();
CatalogComponent catalogComponent = new CatalogComponent();
catalogComponent.setComponent(componentId);
catalogComponent.setComponentType(samplesProperties.getProperty("rest.client.component.type"));
catalogComponent.setLocation(samplesProperties.getProperty("rest.client.component.location"));
catalogComponentList.add(catalogComponent);
return catalogComponentList;
}
/**
* Create a sensor list
*
* @param componentId The Sample Component Id
* @param sensorsIdList A list with the sensor ids to create
* @return A {@link CatalogSensor} list
*/
private List<CatalogSensor> createSensorsList(String providerId, String componentId, List<String> sensorsIdList) {
List<CatalogSensor> catalogSensorsList = new ArrayList<CatalogSensor>();
for (String sensorId : sensorsIdList) {
CatalogSensor catalogSensor = new CatalogSensor();
catalogSensor.setComponent(componentId);
catalogSensor.setSensor(sensorId);
catalogSensor.setProvider(providerId);
catalogSensor.setType(samplesProperties.getProperty("rest.client.sensor.type"));
catalogSensor.setDataType(samplesProperties.getProperty("rest.client.sensor.dataType"));
catalogSensor.setLocation(samplesProperties.getProperty("rest.client.sensor.location"));
catalogSensorsList.add(catalogSensor);
}
return catalogSensorsList;
}
}
What’s happenning?
- First of all, we’re looking for some configuration settings, like the component and sensor names
- Next, we’re using some runtime status values, so we can the publish them as a observations (mem status, for example)
- First of all, we check if the sensor has been created before in the Catalog, and if it doesn’t exists we add it
- After that, we’ll publish the sensor observations
- Then, we pass all this information to the view for displaying it the navigator window
This is an observation sample:
CPU states: 5.8% user, 1.9% system, 0.0% nice, 0.0% wait, 91.7% idle
The samples page view¶
And finally, this is the source code of the view:
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Observations:</h3>
<p>${observations}</p>
<br />
<c:if test="${not empty successMsg}">
<h3>Success:</h3>
<p>${successMsg}</p>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${not empty errorMsg}">
<h3>Error:</h3>
<pre>${errorMsg}</pre>
</c:if>
<br />
<button onclick="location.reload();">Send observations</button>
</body>
</html>
This source code is quite easy, so don’t need to comment it.
Executing the sample application¶
Using the IDE or copying the WAR file, deploy your webbapp into the Tomcat deployments directory, and start it.
You must access to this url (we assume that you’re in your localhost and your port is the 8080, the default values): http://localhost:8080/sentilo-samples (http://localhost:8888/sentilo-samples if using VM )
And then you must see a result page like this:
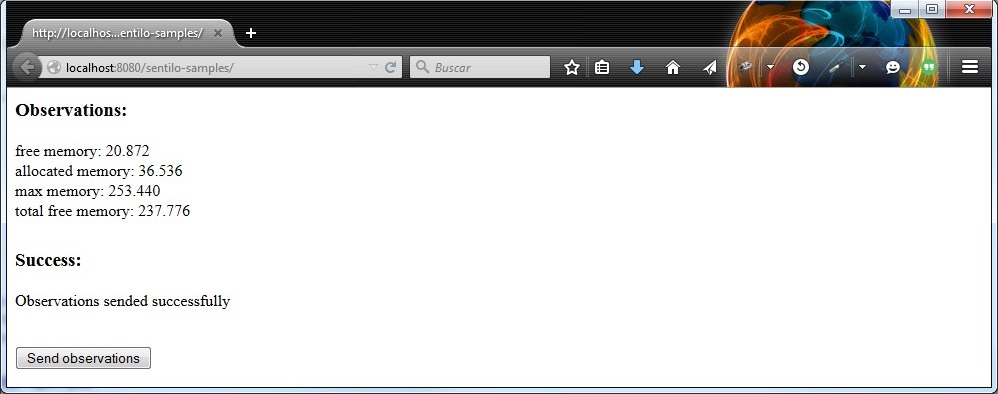
As you can see, there’s a button named Send observations. You can use to re-send observations and reload the page. Every page reload send the observations to the Sentilo Platform Client.
